Innovative Study Highlights BMP9 and SHH as Key Drivers of Bone Repair
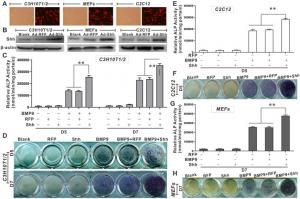
(A) The infection of Ad-Shh in MSCs (fluorescence microscope, × 100). (B) Validation of the expression of Shh by Ad-Shh in MSCs (Western blot). (C, D) The effects of Shh on BMP9-induced ALP activity in C3H10T1/2 cells (C: chemiluminescence; D: cytochemic
New Research Highlights Synergistic Role of BMP9 and Shh in Bone Regeneration
CHINA, March 13, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) directly affect the osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and are integral to bone tissue development. BMP9, a less-studied member of the BMP family, exhibits strong osteogenic effects on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) when combined with growth factors. Sonic Hedgehog (Shh), on the other hand, plays an indispensable role in the regulation of skeletal development.
This research, published in the Genes & Diseases journal by a team from the Chongqing Medical University and People’s Hospital of Deyang City, assesses the potential influence of Shh on BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
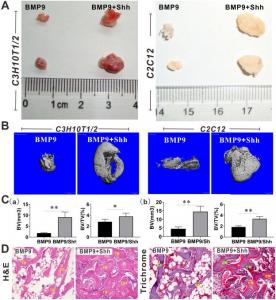
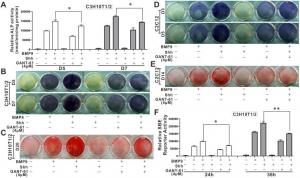
In this study, the researchers found that Shh significantly promoted BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, although Shh alone showed no substantial osteo-inductive effects. In vivo experiments confirmed that Shh significantly promoted BMP9-induced ectopic bone formation in nude mice. Additionally, Shh has been shown to activate osteogenic markers such as Runx2 and ALP in MSCs, further reinforcing its role in bone formation.
The researchers suggest that Shh has the potential to augment BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs by directly affecting the expression/activation of essential osteogenesis-related transcription factors. Furthermore, the findings revealed that Shh increased the transcriptional activity of Smad1/5/8 induced by BMP9, indicating that Shh may further augment the BMP9-induced activation of the Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway.
Interestingly, the study confirmed that GANT-61, an inhibitor of Gli1 and Gli2, reversed the enhancing effect of Shh on BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, thus identifying Gli1 and Gli2 as key mediators in this process. These findings suggest that the combination of BMP9 and Shh holds great promise in addressing complex bone regeneration challenges.
Since BMP9 is already a recognized potent osteo-inductive factor, its enhanced activity through Shh co-treatment presents a promising therapeutic approach. In conclusion, this research has significant implications for MSC-based regenerative medicine, particularly in treating fracture nonunion, delayed healing, and critical bone defects.
Reference
Title of the original paper - Sonic Hedgehog potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Journal - Genes & Diseases
Genes & Diseases is a journal for molecular and translational medicine. The journal primarily focuses on publishing investigations on the molecular bases and experimental therapeutics of human diseases. Publication formats include full length research article, review article, short communication, correspondence, perspectives, commentary, views on news, and research watch.
DOI - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101308
Funding Information:
Chongqing Young and Middle-aged Medical High-end Talent Project (China) (No. 2019GDRC001) Chongqing Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Leader Project (China) (No. cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0103)
Deyang Science and Technology Foundation (Sichuan, China) (No. 2021SZZ060),
Program for Youth Innovation in Future Medicine of Chongqing Medical University (No. W0086)
# # # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3 | Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases)
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
email us here
Visit us on social media:
Facebook
X
LinkedIn
Instagram
YouTube
Other
Distribution channels: Education, Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals Industry, Science
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Submit your press release