Climate Change and the Future of Lignin Production
How Rising Temperatures Could Impact a Key Natural Resource
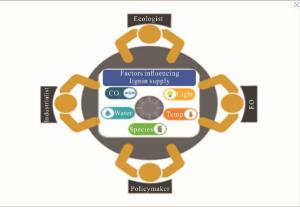
NANJING, CHINA, March 3, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- This mini-review explores the influence of temperature on lignin deposition in plant cell walls, highlighting the need for adaptive strategies in lignin supply chains amidst global warming.Lignin, a complex polymer found in plant cell walls, is the second most abundant organic substance in the plant kingdom after cellulose. It plays a crucial role in providing structural support and defense mechanisms in plants. Industrially, lignin is a by-product of the pulp and paper industry and is increasingly being explored for its potential in biofuels, bioplastics, and advanced materials. However, as global temperatures rise, the production and availability of lignin could be significantly impacted.
The study, titled "Environmental Impacts on Plant Cell Wall Lignification," reviews existing evidence suggesting that lignin deposition is constrained by low temperatures and enhanced by higher temperatures. This has significant implications for industries that rely on lignin, as climate change could alter the availability and characteristics of this resource.
The authors highlight that lignin biosynthesis is a critical evolutionary adaptation that allowed plants to thrive on land. Lignin not only provides mechanical strength but also protects plants from environmental stresses such as drought and herbivory. However, the impact of climate change on lignin production is multifaceted. While low temperatures inhibit lignification, high temperatures appear to promote it, although the latter effect requires further investigation.
The review emphasizes the need for adaptive strategies to ensure a resilient lignin supply chain. This includes understanding regional variations in lignin content, exploring alternative lignin sources, and developing climate-resilient plant varieties. Sustainable forestry and agricultural practices are also crucial in mitigating the impacts of global warming on lignin production.
The study concludes that adapting lignin supply to global warming requires a multifaceted approach involving scientific research, technological innovation, and supportive policy frameworks. By addressing these aspects comprehensively, industries can navigate the complexities of climate change and ensure a sustainable supply of lignin for various applications.
DOI
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2024.11.001
Original Source URL
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2369969824000756
Huicong Cao
Nanjing Forestry University
02585426289
email us here
Visit us on social media:
Facebook
X
LinkedIn
Instagram
YouTube
Other
Distribution channels: Agriculture, Farming & Forestry Industry, Chemical Industry, Environment, Science
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Submit your press release